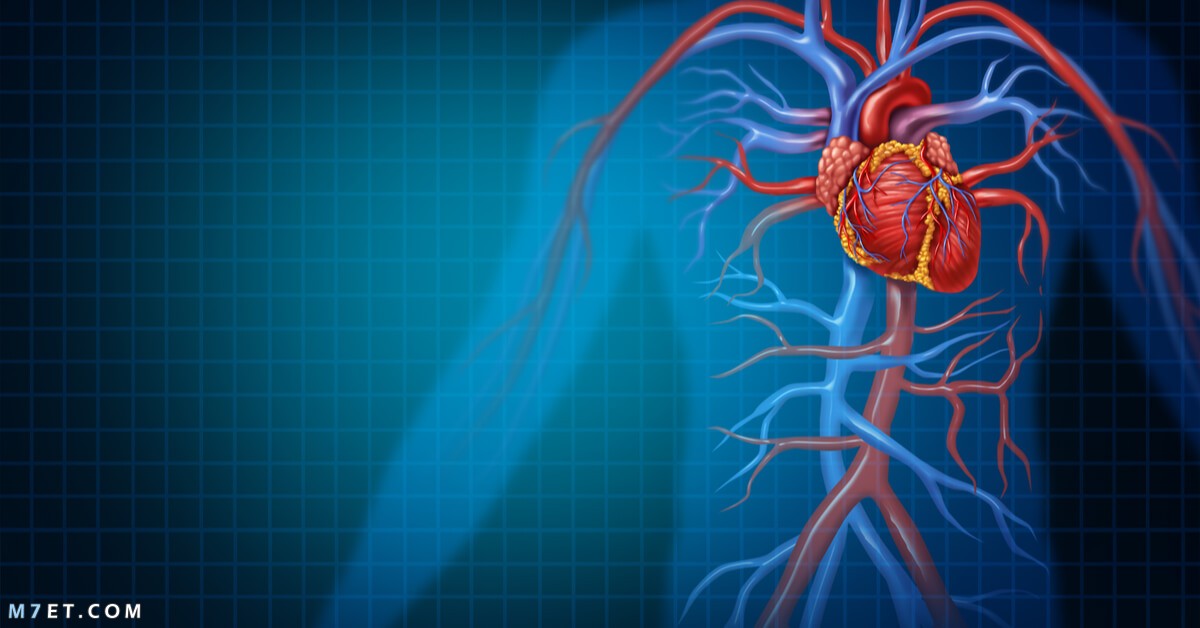
The largest artery in the body through a circumference, The aorta, or what is known as the aorta, is the largest artery in the body. It is divided into four parts. Its function is to transport oxygen-rich blood from the left ventricle of the heart to all parts of the body.
What is the largest artery in the human body?
The largest artery in the body is AortaThe function of the aorta is to transport oxygen-rich blood from the left ventricle of the heart to other parts of the body.
It is the largest artery in the human body 3 names
The largest artery in the human body has three different names, the most famous of which is the aorta or aorta and is known in literary terms as the lutein, and this artery consists of four parts, they are:
- Ascending aorta: It begins at the sinus-tubular junction of the aortic root and extends upward and out of the heart until it connects to the aortic arch, and is about five centimeters long.
- Aortic arch: It is an arch-shaped part of the aorta and connects the ascending aorta to the descending aorta.
- descending aorta: It begins at the end of the aortic arch and continues down the abdomen, supplying blood to the muscles of the chest wall and spinal cord.
- Abdominal aorta: It extends from the diaphragm and ends just above the pelvis, where it divides into branching arteries.
You may be interested in reading: The difference between an artery, a vein, and a capillary
The aorta is the most important artery in the heart
The most important artery in the heart is called the aorta, and its wall consists of three layers of tissue:
- The inner layer: Thin and composed of endothelial cells and underlying supportive tissue.
- Middle class: The largest part of the wall and consists of elastic fibers, smooth muscle and collagen tissue.
- outer layer: The outermost component of the arterial wall, containing mostly connective tissue and a few small blood vessels.
The main arteries in the body
The heart is the organ that helps provide blood and oxygen to all parts of the body. The blood is delivered in the body through a group of major arteries, and they are:
- Aorta:
-
- It is the most important and largest artery in the body; Because (it feeds the heart with oxygen from the arteries branching from the ascending aorta – nourishes the head, neck and hands from the arteries branching from the aortic arch – nourishes the stomach, intestines, kidneys and other vital organs from the arteries branching from the abdominal aorta).
- It supplies small branches with blood to reach the ribs and some structures of the chest.
- carotid artery.
- Pulmonary artery.
- arteries of the upper extremity.
- trunk arteries.
- Coronary artery.
Coronary arteries are very important, because any disorder or disease in them can have dangerous effects, such as reducing the flow of oxygen and nutrients to the heart muscle, and can also lead to a heart attack and possibly death.
Diseases of the largest artery in the body
The largest artery in the body is a flexible, stretchable artery, and its width can be more than one inch in some places, but the aorta may be affected by some diseases, such as:
- Aortic sclerosis: It’s caused by a buildup of cholesterol in the wall of the aorta, which poses a risk of stroke.
- Aortic inflammation: Most cases of vasculitis are caused by an overactive immune system.
- Aortic aneurysm: They occur because there is a weakness in the wall of the aorta that allows it to dilate and become like a balloon. The aneurysm is usually slow to grow, but it can be fatal if it ruptures.
- Aortic stenosis: It is a congenital defect that narrows the arteries branching to the hands and feet, which leads to stress on the heart; Due to high blood pressure in the upper body.
- Aortic insufficiency: The aortic valve does not close completely, allowing some blood to flow back into the heart with each beat, which is caused by autoimmune diseases, Marfan syndrome, or endocarditis.
- Aortic regurgitation: Another name for aortic insufficiency, blood is vomited backward through the incompletely closed aortic valve into the left ventricle of the heart.
- Bicuspid aortic valve: 1% to 2% of people have an aortic valve that has two leaves instead of three. The bicuspid aortic valve may lead to aortic insufficiency or aortic stenosis.
Do not miss the opportunity to watch: The causes of the carotid artery pulsation and 6 tips to prevent it
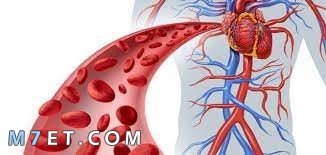
Symptoms of diseases of the largest artery in the body
Most people with diseases of the largest artery in the body do not show any symptoms, but cases that need medical care, develop sudden symptoms, and common signs and symptoms include:
- Sudden, sharp pain in the chest or upper back, also described as a tearing or stabbing feeling.
- Shortness of breath.
- fainting;
- Muted heart sounds.
- High cholesterol.
- Fast and weak pulse.
- heavy sweating;
- vision loss;
- Stroke symptoms, difficulty speaking.
- Sharp pain at the navel, because the largest artery in the body travels from the top of the heart to the bottom of the navel.
- Nausea and vomiting.
Diagnosing diseases of the largest artery in the body
Angiography: It is an angiogram. Using X-rays and contrast material, a catheter is inserted into an artery in the groin and advanced into the aorta.
- Abdominal ultrasound: Through it, an abdominal aortic aneurysm can be detected and measured to estimate the risk of rupture.
- computed tomography (CT scan): An x-ray imaging scanner and a computer are used; To create images of the aorta and surrounding structures.
- Magnetic Resonance: An MRI scanner uses radio waves within a magnetic field to generate images of the aorta.
- Transthoracic echocardiogram: A probe is placed on the chest that releases ultrasound waves from the aorta and heart.
- Transesophageal echocardiogram: The ultrasound probe at the end of the flexible tube is inserted through the mouth and down into the esophagus. Transesophageal echocardiograms allow a better view of the first part of the aorta.
Risk factors for diseases of the largest artery in the human body
Many factors increase the risk of disease in the largest artery in the body, such as:
- Hypertension.
- Genetic factors, such as Marfan syndrome.
- High cholesterol or atherosclerosis.
- Inflamed arteries, such as vasculitis.
- Trauma, such as car accidents.
- smoking; Because it causes aneurysm.
Aortic treatment
Diseases of the largest artery in the body are treated by:
- pharmaceutical: In order to control heart rate and blood pressure, and reduce the risk of developing conditions that require emergency medical care.
- surgery: The surgery is divided into:
- Aortic aneurysm repair: When the aortic aneurysm reaches a certain size, surgery must be performed to prevent rupture, which is done through an incision in the abdomen.
- Aortic grafting: Any damaged part of the aorta can be removed or replaced by bracing it with an artificial mesh.
- Aortic valve replacement: Surgical replacement of a damaged aortic valve.
- Aortic surgery: If the aorta is aneurysm, narrowed, or analyzed, a portion of the aorta is removed.
Aortic surgery success rate
Aortic surgery is performed for patients who suffer from arteriosclerosis or aneurysm, due to chronic blood pressure disorders, or because the patient has a craving for smoking, and the success rate of the aortic operation depends on the patient’s condition.
But according to statistics, more than 80% of patients recover, and this percentage increases, of course, if there are factors of skill, competence and experience in the surgeon who performs the operation.
[ad_2]